Our Technology
Advancing Electron Microscopy with cutting-edge imaging & subsampling software
SenseAI is democratising electron microscopy (EM) and other scientific imaging methods, reducing burden and complexity for scientists and engineers. We apply proprietary sparse sampling workflows to leverage exquisite control of beam dose, image capture, and processing…all in real time.
capabilitiesSenseAI is a suite of AI technologies that transforms imaging and subsampling in EM
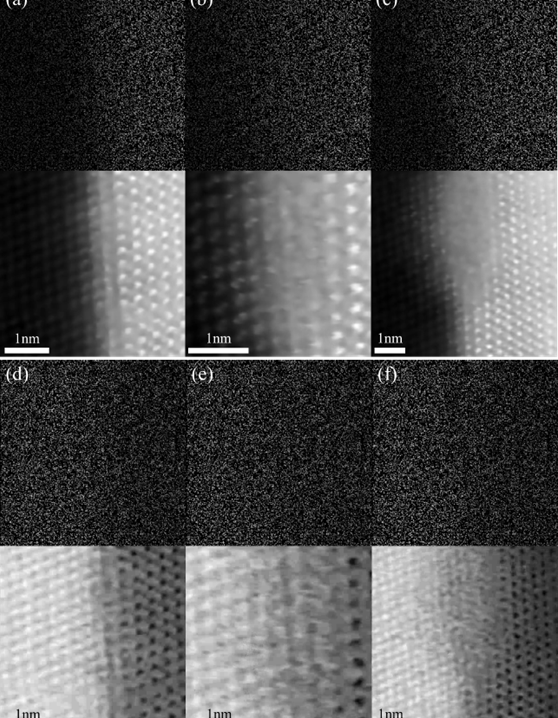
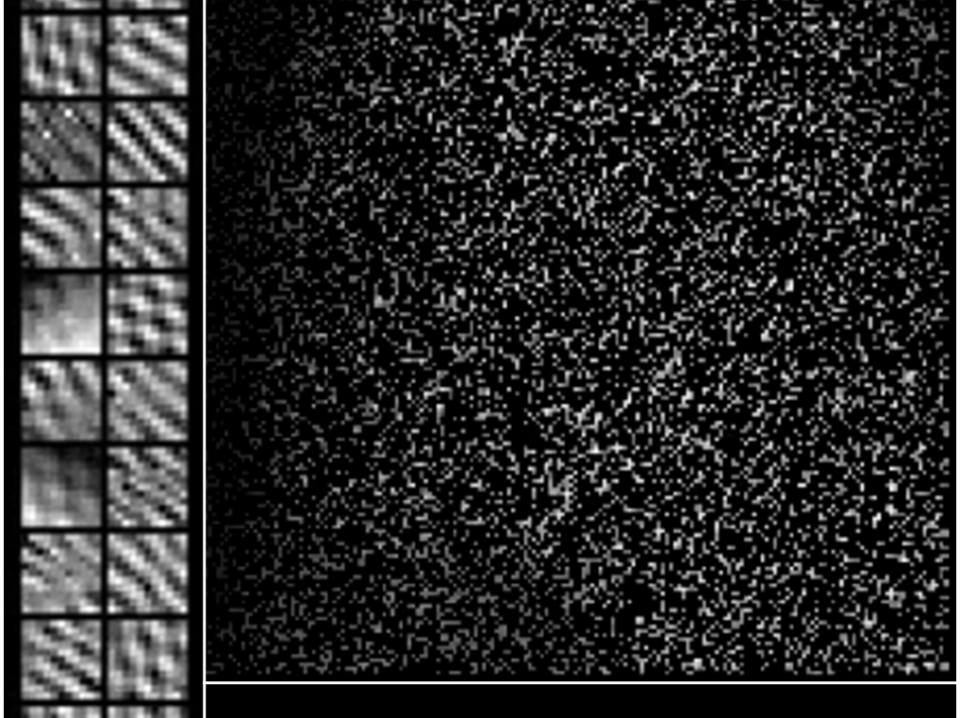
Using proprietary sub-sampling methodologies, SenseAI can generate the same high-quality images and video feeds with up to 100x less data (1% of the original data). This can massively speed up the imaging process.
SenseAI can unlock automation and other capabilities too. For applications where beam damage is an issue, SenseAI is low dose and this preserves sample integrity.
Patented Technology
SenseAI is based on decades of academic research globally and more recently at University of Liverpool in the UK. The core technology is embodied in a series of patents as well as software knowhow developed over a long period.
Inpainting Algorithm
Sub-sampling techniques initially take random samples of the image which is then complemented by an ultra-fast implementation of an inpainting algorithm, developed from the ground up to be a world leader in high quality image inpainting applications, as well as flexible enough to be robust across a wide range of applications.
Easy Implementation
No lengthy or costly training data is required, and the methods can be implemented with a push of a button.
servicesThe unique selling points & advantages of our service
about usExpert ai consulting for transformative business solutions with Neuros
Artificial Intelligence refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. It involves the creation of algorithms and models that enable machines to learn, reason, perceive, and make decisions.
There are generally two types of AI: Narrow or Weak AI, which is designed to perform specific tasks, and General or Strong AI, which possesses human-level intelligence and can handle a wide range of tasks.
How does SenseAI work?
At its core, SenseAI utilises an ultra-fast implementation of the beta process factor analysis (BPFA) algorithm. BPFA is used to learn a sparse representation of a dataset, which is then used to reconstruct that entire dataset. Unlike many other algorithms, BPFA is a blind inpainting algorithm, meaning that it can learn a dictionary from both fully sampled and subsampled data.
What is subsampling?
Subsampling is a core component of the SenseAI workflow, and involves the deliberate formation of incomplete datasets. By sampling a fraction of the data, such as only a handful of pixels within an image, subsampled data can be produced and processed using SenseAI. Subsampling can be achieved by manipulating scanning hardware, implementing novel detector designs, or operating in low signal conditions, and in almost all cases can aid in increasing the speed of data acquisition.
What can SenseAI be used for?
Subsampling can be applied to nearly every imaging platform, though the form it takes will depend on the system. In all cases, an incomplete dataset is formed – this means faster acquisition times and faster processing times. In scanning systems, the imaging flux can also be reduced, meaning that not only can information be acquired faster, but with less damage to sensitive materials.
What issues can SenseAI solve?
- High and excessive electron doses
- Beam-sensitive materials
- Slow acquisition speeds
- Low signal to noise
- Burdensome & expensive data volumes
projectsPioneering projects for Intelligent solutions
 DeepVision: Enhancing image recognition with Neural NetworksNeural networks are a fundamental component of Artificial IntelliExplore more
DeepVision: Enhancing image recognition with Neural NetworksNeural networks are a fundamental component of Artificial IntelliExplore more
 AutoDrive: Autonomous vehicle navigation with advanced Neural NetworksIntegrating neural network models into existing systems or softwaExplore more
AutoDrive: Autonomous vehicle navigation with advanced Neural NetworksIntegrating neural network models into existing systems or softwaExplore more
 HealthCareAI: Personalized diagnostics and treatment recommendations with Neural NetworksIntegrating neural network models into existing systems or softwaExplore more
HealthCareAI: Personalized diagnostics and treatment recommendations with Neural NetworksIntegrating neural network models into existing systems or softwaExplore more
pricingSimple and flexible.
Only pay for what you use.
User stories: hear what others love about our WordPress themes!
manojchouh
Nice theme with excellent support from the developers. All of my doubts and requests were fixed within a day.
elkab 3
Amazing customer support. I had one modifications and the customer support was super helpful and quick to answer them both.
tolunayc
code quality very high and they have very detailed documentaion also they have very corporate for customer ticket
hikevin2000
the customer suport is excellent!Thank you Sergey for your quick response and everything you did for me!
metintahayilma
A perfect theme in every respect. They are very good especially in terms of support. I definitely recommend it. I bought dozens of themes. If I put them all on top of each other, it can’t catch the success of this theme.
khoavo
This is one of the best Theme I’ve purchased thus far. And the customer support by the Author is first-class. Very professional and attentive to my needs. Thanks for sharing your work.
sinilian
Wonderful and clean design will create an excellent base for starting the new agency. Especially when you don’t want to do design turnkey and are looking for something to help you make a fast and easy launch.
kerim80
Fast and good support.Theme easy to customize and many usable custom Elementor theme widgets.Nice work.
powert
Great renewable energy theme for business.I recommend this Energium theme because it is very well-designed and easy to configure with elementor, and apply your own design.
Great job.
manojchouh
Nice theme with excellent support from the developers. All of my doubts and requests were fixed within a day.
emil_b
Great theme, and great customer support!The author always provided a solution even though it was not theme related.
I’ll surely buy new WordPress themes from Artureanec.
startelectric2022
I purchased the theme because I really liked the design. After I started working with it I realized that I needed to translate some elements into Romanian.
hikevin2000
the customer suport is excellent!Thank you Sergey for your quick response and everything you did for me!
metintahayilma
A perfect theme in every respect. They are very good especially in terms of support. I definitely recommend it. I bought dozens of themes. If I put them all on top of each other, it can’t catch the success of this theme.
khoavo
This is one of the best Theme I’ve purchased thus far. And the customer support by the Author is first-class. Very professional and attentive to my needs. Thanks for sharing your work.
manojchouh
Nice theme with excellent support from the developers. All of my doubts and requests were fixed within a day.
emil_b
Great theme, and great customer support!The author always provided a solution even though it was not theme related.
I’ll surely buy new WordPress themes from Artureanec.
startelectric2022
I purchased the theme because I really liked the design. After I started working with it I realized that I needed to translate some elements into Romanian.